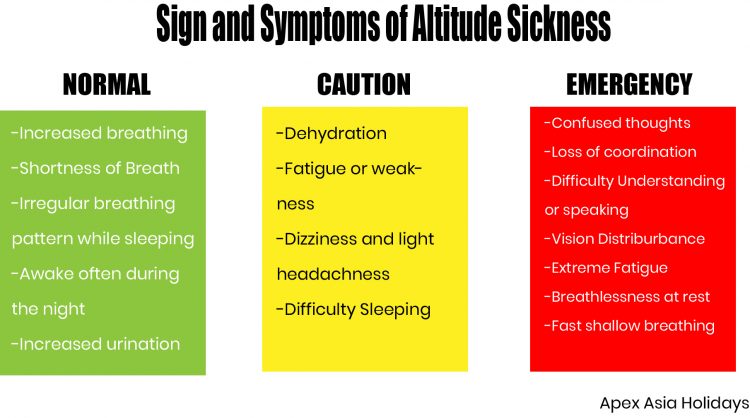
What is Acute Mountain Sickness? Signs & Symptoms
Acute mountain sickness(AMS), is also known as Altitude Sickness, is a severe medical condition that occurs at high elevations.
If you plan on trekking to high altitudes, you must understand the signs and symptoms of the condition of the sickness. In this article, we provide you with general information on AMS. What is altitude sickness, and how it works, and what to do if it happens to you? Through the article, we also provide you with remedies and supplements you can use to reduce the chances of developing the conditions while you are on the High Himalayas.
What Causes Acute Mountain Sickness / Altitude Sickness?
Acute mountain sickness is because by reduced air pressure and lower oxygen levels at high elevations. The faster you climb to a high altitude, the more likely you will get acute mountain sickness. The best way to prevent altitude illness is to ascend gradually.
The best way of escaping AMS is to spend at least two days ascending to 9850 feet (3000). Above this point ascend very slowly and try to do not to increase more than 990 feet to 1640 feet (300m to 500m) per night.
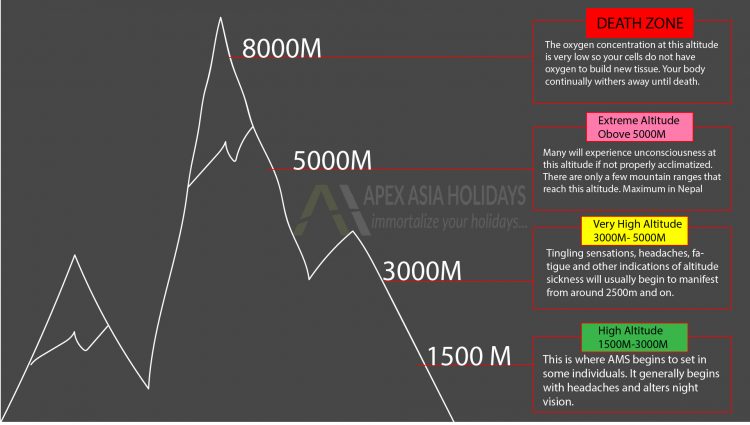
This is where AMS begins to set in some individuals. It generally begins with headaches and alters night vision.
Tingling sensations, headaches, fatigue and other indications of altitude sickness will usually begin to manifest
from around 2500m and on.
Many will experience unconsciousness at this altitude if not properly acclimatized. There are only a few mountain ranges that reach this altitude. Maximum in Nepal
The oxygen concentration at this altitude is very low so your cells do not have oxygen to build new tissue. Your body continually withers away until death.